Qt에서 쓰레드를 생성하는 방법은 몇가지가 있는데 여기서는 QtConcurrent를 이용한 벙법을 소개한다.
예제소스이다
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <qtconcurrentrun.h>
#include <QThread>
#ifndef QT_NO_CONCURRENT
void myRunFunction(QString name)
{
for(int i = 0; i <= 5; i++)
{
qDebug() << name << " " << i <<
"from" << QThread::currentThread();
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
QFuture<void> t1 = QtConcurrent::run(myRunFunction, QString("A"));
QFuture<void> t2 = QtConcurrent::run(myRunFunction, QString("B"));
QFuture<void> t3 = QtConcurrent::run(myRunFunction, QString("C"));
t1.waitForFinished();
t2.waitForFinished();
t3.waitForFinished();
return a.exec();
}
#else
#include <QLabel>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
QString text("Qt Concurrent is not yet supported on this platform");
QLabel *label = new QLabel(text);
label->setWordWrap(true);
label->show();
qDebug() << text;
app.exec();
}
#endif
.pro파일에는 아래와 같은 행을 추가 해야한다.
QT += concurrent
예제에서 볼 수 있듯이 Worker쓰레드를 만들거나 Qthread를 생성할 필요없이 단지 할 일은 적절한 매개변수 전달과 실행될 함수를 정의하는 것이다. 예제에서 QtConcurrent의 아래와 같은 API들을 사용했다.
QtConcurrent::run() - 다른 쓰레드에서 함수를 실행한다.
QFuture - 비동기의 결과를 제어하는 클래스이다.
QFuture는 실제로 waitForFinished()<결과를 기다리거나>, result()<결과 값을 확인하거나>, cancel(), pause(), or resume()등의 메소드들을 제공한다.
주의할 점은 QtConcurrent::run()으로 얻은 future객체는 cancel, pause and resum을 지원하지않는다.
그러면 MapReduce는 무엇인가.
MapReduce는 대용량 데이터의 병렬처리 알고리즘을 단순화하기 위해 구글에서 고안했다.
병렬 분산 알고리즘을 사용하여 빅 데이터 세트를 처리하고 생성하기위한 프로그래밍 모델 및 관련 구현인것이다.
QtConcurrent 프레임웍은 이러한 병렬처리를 위한 방법으로 mappedReduced를 제공한다.
API는 다음과 같다.
QFuture<T> mappedReduced(list, mapFunction, reducefunction);
기본 개념은 알고리즘을 두 부분으로 나누는 것인데,
하나는 입력 데이터의 개별 부분에서 병렬로 실행할 수있는 부분(map)과 또 하나는 결과를 수집하고 최종 결과를 생성하는 하나의 순차적 파트(reduce)가 그것이다.
아래는 Qt기본 예제인데 map-reduce 알고리즘을 사용하는 방법을 보여준다.
먼저 파일 목록이 입력될 목록으로 사용된다.
QStringList files = findFiles("../../", QStringList() << "*.cpp" << "*.h");
그런다음 기본 싱글 쓰레드로 파일 목록의 단어수를 카운팅한다.
typedef QMap<QString, int> WordCount;
WordCount singleThreadedWordCount(const QStringList &files)
{
WordCount wordCount;
for (const QString &file : files) {
QFile f(file);
f.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly);
QTextStream textStream(&f);
while (!textStream.atEnd()) {
const auto words = textStream.readLine().split(' ');
for (const QString &word : words)
wordCount[word] += 1;
}
}
return wordCount;
}
int singleThreadTime = 0;
{
QTime time;
time.start();
WordCount total = singleThreadedWordCount(files);
singleThreadTime = time.elapsed();
qDebug() << "single thread" << singleThreadTime;
}
그리고 mappedReduced API를 사용하여 역시 파일목록의 단어수를 카운팅한다.
WordCount countWords(const QString &file)
{
QFile f(file);
f.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly);
QTextStream textStream(&f);
WordCount wordCount;
while (!textStream.atEnd()) {
const auto words = textStream.readLine().split(' ');
for (const QString &word : words)
wordCount[word] += 1;
}
return wordCount;
}
void reduce(WordCount &result, const WordCount &w)
{
QMapIterator<QString, int> i(w);
while (i.hasNext()) {
i.next();
result[i.key()] += i.value();
}
}
int mapReduceTime = 0;
{
QTime time;
time.start();
WordCount total = mappedReduced(files, countWords, reduce);
mapReduceTime = time.elapsed();
qDebug() << "MapReduce" << mapReduceTime;
}
위의 예제를 컴파일해서 실행해본 결과이다.
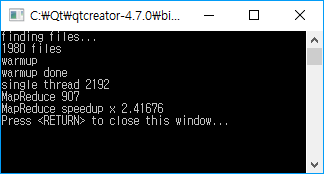
싱글 쓰레드 카운팅연산에 비해 map-reduce 알고리즘에 의해 처리된 시간이 2배가 넘게 빠른 결과를 보여준다.
QtConcurrent 및 MapReduce의 좀더 자세한 내용은 해당사이트를 참고하기 바란다.
http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtconcurrent-index.html